Request queue
Queue URLs for an Actor to visit in its run. Learn how to share your queues between Actor runs. Access and manage request queues from Apify Console or via API.
Request queues enable you to enqueue and retrieve requests such as URLs with an HTTP method and other parameters. They prove essential not only in web crawling scenarios but also in any situation requiring the management of a large number of URLs and the addition of new links.
The storage system for request queues accommodates both breadth-first and depth-first crawling strategies, along with the inclusion of custom data attributes. This system enables you to check if certain URLs have already been encountered, add new URLs to the queue, and retrieve the next set of URLs for processing.
Named request queues are retained indefinitely.
Unnamed request queues expire after 7 days unless otherwise specified.
> Learn more
Basic usage
You can access your request queues in several ways:
- Apify Console - provides an easy-to-understand interface.
- Apify API - for accessing your request queues programmatically.
- Apify API clients - to access your request queues from any Node.js application.
- Apify SDK - when building your own JavaScript Actor.
Apify Console
In the Apify Console, you can view your request queues in the Storage section under the Request queues tab.
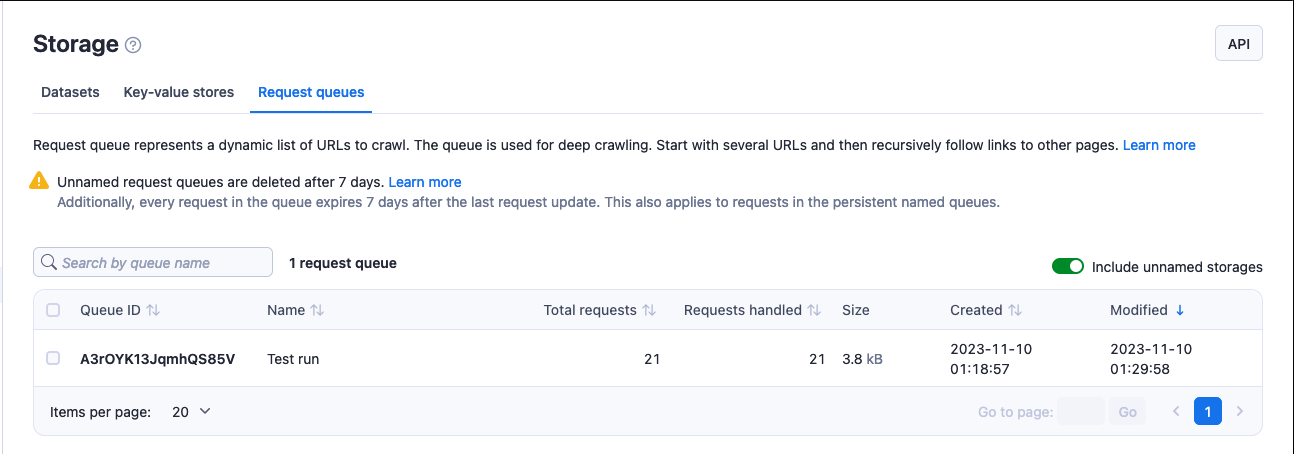
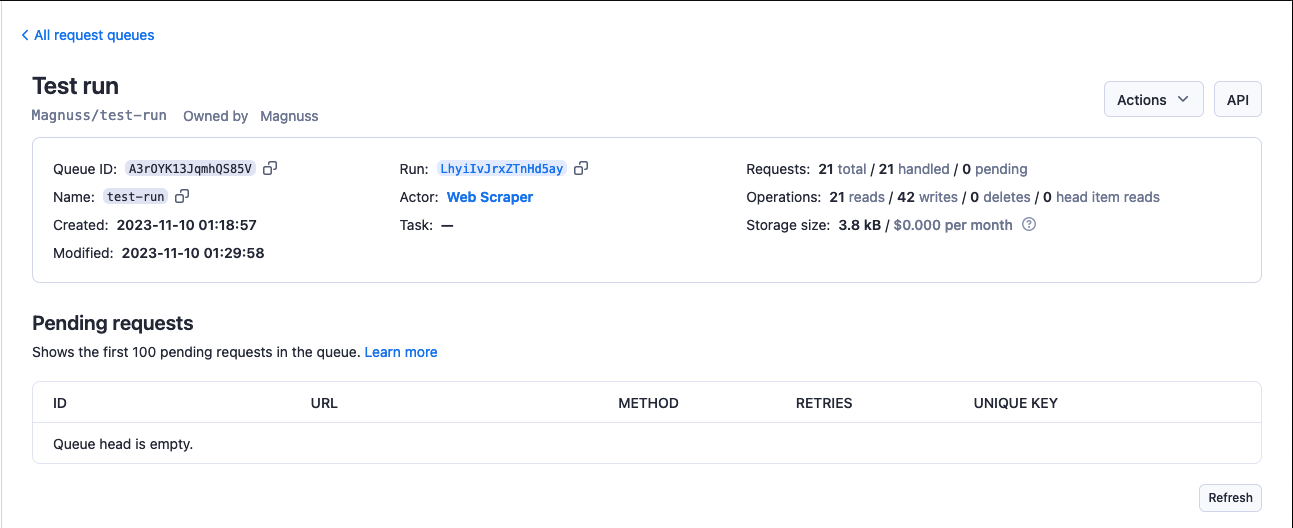
To view a request queue, click on its Queue ID. Under the Actions menu, you can rename your queue's name (and, in turn, its retention period) and access rights using the Share button. Click on the API button to view and test a queue's API endpoints.
Apify API
The Apify API allows you programmatic access to your request queues using HTTP requests.
If you are accessing your datasets using the username~store-name store ID format, you will need to use your secret API token. You can find the token (and your user ID) on the Integrations page of your Apify account.
When providing your API authentication token, we recommend using the request's
Authorizationheader, rather than the URL. (More info).
To get a list of your request queues, send a GET request to the Get list of request queues endpoint.
https://api.apify.com/v2/request-queues
To get information about a request queue such as its creation time and item count, send a GET request to the Get request queue endpoint.
https://api.apify.com/v2/request-queues/{QUEUE_ID}
To get a request from a queue, send a GET request to the Get request endpoint.
https://api.apify.com/v2/request-queues/{QUEUE_ID}/requests/{REQUEST_ID}
To add a request to a queue, send a POST request with the request to be added as a JSON object in the request's payload to the Add request endpoint.
https://api.apify.com/v2/request-queues/{QUEUE_ID}/requests
Example payload:
{
"uniqueKey": "http://example.com",
"url": "http://example.com",
"method": "GET"
}
To update a request in a queue, send a PUT request with the request to update as a JSON object in the request's payload to the Update request endpoint. In the payload, specify the request's ID and add the information you want to update.
https://api.apify.com/v2/request-queues/{QUEUE_ID}/requests/{REQUEST_ID}
Example payload:
{
"id": "dnjkDMKLmdlkmlkmld",
"uniqueKey": "http://example.com",
"url": "http://example.com",
"method": "GET"
}
When adding or updating requests, you can optionally provide a
clientKeyparameter to your request. It must be a string between 1 and 32 characters in length. This identifier is used to determine whether the queue was accessed by multiple clients. IfclientKeyis not provided, the system considers this API call to come from a new client. See thehadMultipleClientsfield returned by theGet headoperation for details.Example:
client-abc
For further details and a breakdown of each storage API endpoint, refer to the API documentation.
Apify API Clients
JavaScript API client
The Apify JavaScript API client (apify-client) enables you to access your request queues from any Node.js application, whether it is running on the Apify platform or externally.
After importing and initiating the client, you can save each request queue to a variable for easier access.
const myQueueClient = apifyClient.requestQueue('jane-doe/my-request-queue');
You can then use that variable to access the request queue's items and manage it.
Check out the JavaScript API client documentation for help with setup and more details.
Python API client
The Apify Python API client (apify-client) allows you to access your request queues from any Python application, whether it's running on the Apify platform or externally.
After importing and initiating the client, you can save each request queue to a variable for easier access.
my_queue_client = apify_client.request_queue('jane-doe/my-request-queue')
You can then use that variable to access the request queue's items and manage it.
Check out the Python API client documentation for help with setup and more details.
Apify SDKs
JavaScript SDK
When working with a JavaScript Actor, the JavaScript SDK is an essential tool, especially for request queue management. The primary class for this purpose is the RequestQueue class. Use this class to decide whether your data is stored locally or in the Apify cloud.
If you are building a JavaScript Actor, you will be using the JavaScript SDK. The request queue is represented by a RequestQueue class. You can use the class to specify whether your data is stored locally or in the Apify cloud and enqueue new URLs.
Every Actor run is automatically linked with a default request queue, initiated upon adding the first request. This queue is primarily utilized for storing URLs to be crawled during the particular Actor run, though its use is not mandatory. For enhanced flexibility, you can establish named queues. These named queues offer the advantage of being shareable across different Actors or various Actor runs, facilitating a more interconnected and efficient process.
If you are storing your data locally, you can find your request queue at the following location.
{APIFY_LOCAL_STORAGE_DIR}/request_queues/{QUEUE_ID}/{ID}.json
The default request queue's ID is default. Each request in the queue is stored as a separate JSON file, where {ID} is a request ID.
To open a request queue, use the Actor.openRequestQueue() method.
// Import the JavaScript SDK into your project
import { Actor } from 'apify';
await Actor.init();
// ...
// Open the default request queue associated with
// the Actor run
const queue = await Actor.openRequestQueue();
// Open the 'my-queue' request queue
const queueWithName = await Actor.openRequestQueue('my-queue');
// ...
await Actor.exit();
Once a queue is open, you can manage it using the following methods. Check out the RequestQueue class's API reference for the full list.
// Import the JavaScript SDK into your project
import { Actor } from 'apify';
await Actor.init();
// ...
const queue = await Actor.openRequestQueue();
// Enqueue requests
await queue.addRequests([{ url: 'http://example.com/aaa' }]);
await queue.addRequests(['http://example.com/foo', 'http://example.com/bar'], {
forefront: true,
});
// Get the next request from queue
const request1 = await queue.fetchNextRequest();
const request2 = await queue.fetchNextRequest();
// Get a specific request
const specificRequest = await queue.getRequest('shi6Nh3bfs3');
// Reclaim a failed request back to the queue
// and process it again
await queue.reclaimRequest(request2);
// Remove a queue
await queue.drop();
// ...
await Actor.exit();
Check out the JavaScript SDK documentation and the RequestQueue class's API reference for details on managing your request queues with the JavaScript SDK.
Python SDK
For Python Actor development, the Python SDK the in essential. The request queue is represented by RequestQueue class. Utilize this class to determine whether your data is stored locally or in the Apify cloud. For managing your data, it provides the capability to enqueue new URLs, facilitating seamless integration and operation within your Actor.
Every Actor run is automatically connected to a default request queue, established specifically for that run upon the addition of the first request. If you're operating your Actors and choose to utilize this queue, it typically serves to store URLs for crawling in the respective Actor run, though its use is not mandatory. To extend functionality, you have the option to create named queue, which offer the flexibility to be shared among different Actors or across multiple Actor runs.
If you are storing your data locally, you can find your request queue at the following location.
{APIFY_LOCAL_STORAGE_DIR}/request_queues/{QUEUE_ID}/{ID}.json
The default request queue's ID is default. Each request in the queue is stored as a separate JSON file, where {ID} is a request ID.
To open a request queue, use the Actor.open_request_queue() method.
from apify import Actor
async def main():
async with Actor:
# Open the default request queue associated with the Actor run
queue = await Actor.open_request_queue()
# Open the 'my-queue' request queue
queue_with_name = await Actor.open_request_queue(name='my-queue')
# ...
Once a queue is open, you can manage it using the following methods. See the RequestQueue class's API reference for the full list.
from apify import Actor
from apify.storages import RequestQueue
async def main():
async with Actor:
queue: RequestQueue = await Actor.open_request_queue()
# Enqueue requests
await queue.add_request(request={'url': 'http:#example.com/aaa'})
await queue.add_request(request={'url': 'http:#example.com/foo'})
await queue.add_request(request={'url': 'http:#example.com/bar'}, forefront=True)
# Get the next requests from queue
request1 = await queue.fetch_next_request()
request2 = await queue.fetch_next_request()
# Get a specific request
specific_request = await queue.get_request('shi6Nh3bfs3')
# Reclaim a failed request back to the queue and process it again
await queue.reclaim_request(request2)
# Remove a queue
await queue.drop()
Check out the Python SDK documentation and the RequestQueue class's API reference for details on managing your request queues with the Python SDK.
Features
Request queue is a storage type built with scraping in mind, enabling developers to write scraping logic efficiently and scalably. The Apify tooling, including Crawlee, Apify SDK for JavaScript, and Apify SDK for Python, incorporates all these features, enabling users to leverage them effortlessly without extra configuration.
In the following section, we will discuss each of the main features in depth.
Persistence and retention
Request queues prioritize persistence, ensuring indefinite retention of your requests in named request queues, and for the data retention period in your subscription in unnamed request queues. This capability facilitates incremental crawling, where you can append new URLs to the queue and resume from where you stopped in subsequent Actor runs. Consider the scenario of scraping an e-commerce website with thousands of products. Incremental scraping allows you to scrape only the products added since the last product discovery.
In the following code example, we demonstrate how to use the Apify SDK and Crawlee to create an incremental crawler that saves the title of each new found page in Apify Docs to a dataset. By running this Actor multiple times, you can incrementally crawl the source website and save only pages added since the last crawl, as reusing a single request queue ensures that only URLs not yet visited are processed.
// Basic example of incremental crawling with Crawlee.
import { Actor } from 'apify';
import { CheerioCrawler, Dataset } from 'crawlee';
interface Input {
startUrls: string[];
persistRequestQueueName: string;
}
await Actor.init();
// Structure of input is defined in input_schema.json
const {
startUrls = ['https://docs.apify.com/'],
persistRequestQueueName = 'persist-request-queue',
} = (await Actor.getInput<Input>()) ?? ({} as Input);
// Open or create request queue for incremental scrape.
// By opening same request queue, the crawler will continue where it left off and skips already visited URLs.
const requestQueue = await Actor.openRequestQueue(persistRequestQueueName);
const proxyConfiguration = await Actor.createProxyConfiguration();
const crawler = new CheerioCrawler({
proxyConfiguration,
requestQueue, // Pass incremental request queue to the crawler.
requestHandler: async ({ enqueueLinks, request, $, log }) => {
log.info('enqueueing new URLs');
await enqueueLinks();
// Extract title from the page.
const title = $('title').text();
log.info(`New page with ${title}`, { url: request.loadedUrl });
// Save the URL and title of the loaded page to the output dataset.
await Dataset.pushData({ url: request.loadedUrl, title });
},
});
await crawler.run(startUrls);
await Actor.exit();
Batch operations
Request queues support batch operations on requests to enqueue or retrieve multiple requests in bulk, to cut down on network latency and enable easier parallel processing of requests. You can find the batch operations in the Apify API, as well in the Apify API client for JavaScript and Python.
- JavaScript
- Python
const { ApifyClient } = require('apify-client');
const client = new ApifyClient({
token: 'MY-APIFY-TOKEN',
});
const requestQueueClient = client.requestQueue('my-queue-id');
// Add multiple requests to the queue
await requestQueueClient.batchAddRequests([
{
url: 'http://example.com/foo',
uniqueKey: 'http://example.com/foo',
method: 'GET',
},
{
url: 'http://example.com/bar',
uniqueKey: 'http://example.com/bar',
method: 'GET',
},
]);
// Remove multiple requests from the queue
await requestQueueClient.batchDeleteRequests([
{ uniqueKey: 'http://example.com/foo' },
{ uniqueKey: 'http://example.com/bar' },
]);
from apify_client import ApifyClient
apify_client = ApifyClient('MY-APIFY-TOKEN')
request_queue_client = apify_client.request_queue('my-queue-id')
# Add multiple requests to the queue
request_queue_client.batch_add_requests([
{'url': 'http://example.com/foo', 'uniqueKey': 'http://example.com/foo', 'method': 'GET'},
{'url': 'http://example.com/bar', 'uniqueKey': 'http://example.com/bar', 'method': 'GET'},
])
# Remove multiple requests from the queue
request_queue_client.batch_delete_requests([
{'uniqueKey': 'http://example.com/foo'},
{'uniqueKey': 'http://example.com/bar'},
])
Distributivity
Request queue includes a locking mechanism to avoid concurrent processing of one request by multiple clients (for example Actor runs). You can lock a request so that no other clients receive it when they fetch the queue head, with an expiration period on the lock so that requests which fail processing are eventually unlocked and retried.
This feature is seamlessly integrated into Crawlee, requiring minimal extra setup. By default, requests are locked for the same duration as the timeout for processing requests in the crawler (requestHandlerTimeoutSecs).
If the Actor processing the request fails, the lock expires, and the request is processed again eventually. For more details, refer to the Crawlee documentation.
In the following example, we demonstrate how you can use locking mechanisms to avoid concurrent processing of the same request across multiple Actor runs.
The lock mechanism works on the client level, as well as the run level, when running the Actor on the Apify platform.
This means you can unlock or prolong the lock the locked request only if:
- You are using the same client key, or
- The operation is being called from the same Actor run.
- Actor 1
- Actor 2
import { Actor, ApifyClient } from 'apify';
await Actor.init();
const client = new ApifyClient({
token: 'MY-APIFY-TOKEN',
});
// Creates a new request queue.
const requestQueue = await client.requestQueues().getOrCreate('example-queue');
// Creates two clients with different keys for the same request queue.
const requestQueueClient = client.requestQueue(requestQueue.id, {
clientKey: 'requestqueueone',
});
// Adds multiple requests to the queue.
await requestQueueClient.batchAddRequests([
{
url: 'http://example.com/foo',
uniqueKey: 'http://example.com/foo',
method: 'GET',
},
{
url: 'http://example.com/bar',
uniqueKey: 'http://example.com/bar',
method: 'GET',
},
{
url: 'http://example.com/baz',
uniqueKey: 'http://example.com/baz',
method: 'GET',
},
{
url: 'http://example.com/qux',
uniqueKey: 'http://example.com/qux',
method: 'GET',
},
]);
// Locks the first two requests at the head of the queue.
const processingRequestsClientOne = await requestQueueClient.listAndLockHead(
{
limit: 2,
lockSecs: 120,
},
);
// Checks when the lock will expire. The locked request will have a lockExpiresAt attribute.
const lockedRequest = processingRequestsClientOne.items[0];
const lockedRequestDetail = await requestQueueClient.getRequest(
lockedRequest.id,
);
console.log(`Request locked until ${lockedRequestDetail?.lockExpiresAt}`);
// Prolongs the lock of the first request or unlocks it.
await requestQueueClient.prolongRequestLock(
lockedRequest.id,
{ lockSecs: 120 },
);
await requestQueueClient.deleteRequestLock(
lockedRequest.id,
);
await Actor.exit();
import { Actor, ApifyClient } from 'apify';
await Actor.init();
const client = new ApifyClient({
token: 'MY-APIFY-TOKEN',
});
// Waits for the first Actor to lock the requests.
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
// Get the same request queue in different Actor run and with a different client key.
const requestQueue = await client.requestQueues().getOrCreate('example-queue');
const requestQueueClient = client.requestQueue(requestQueue.id, {
clientKey: 'requestqueuetwo',
});
// Get all requests from the queue and check one locked by the first Actor.
const requests = await requestQueueClient.listRequests();
const requestsLockedByAnotherRun = requests.items.filter((request) => request.lockByClient === 'requestqueueone');
const requestLockedByAnotherRunDetail = await requestQueueClient.getRequest(
requestsLockedByAnotherRun[0].id,
);
// Other clients cannot list and lock these requests; the listAndLockHead call returns other requests from the queue.
const processingRequestsClientTwo = await requestQueueClient.listAndLockHead(
{
limit: 10,
lockSecs: 60,
},
);
const wasBothRunsLockedSameRequest = !!processingRequestsClientTwo.items.find(
(request) => request.id === requestLockedByAnotherRunDetail.id,
);
console.log(`Was the request locked by the first run locked by the second run? ${wasBothRunsLockedSameRequest}`);
console.log(`Request locked until ${requestLockedByAnotherRunDetail?.lockExpiresAt}`);
// Other clients cannot modify the lock; attempting to do so will throw an error.
try {
await requestQueueClient.prolongRequestLock(
requestLockedByAnotherRunDetail.id,
{ lockSecs: 60 },
);
} catch (err) {
// This will throw an error.
}
// Cleans up the queue.
await requestQueueClient.delete();
await Actor.exit();
A detailed tutorial on how to process one request queue with multiple Actor runs can be found in Academy tutorials.
Share
You can grant access rights to your request queue through the Share button under the Actions menu. For more details check the full list of permissions.
You can also share request queues by link using their ID or name, depending on your account or resource-level general access setting. Learn how link-based access works in General resource access.
For one-off sharing of specific records when access is restricted, you can generate time-limited pre-signed URLs. See Sharing restricted resources with pre-signed URLs.
Share request queues between runs
You can access a request queue from any Actor or task run as long as you know its name or ID.
To access a request queue from another run using the Apify SDK, open it using the same method like you would do with any other request queue.
- JavaScript
- Python
import { Actor } from 'apify';
await Actor.init();
const otherQueue = await Actor.openRequestQueue('old-queue');
// ...
await Actor.exit();
from apify import Actor
async def main():
async with Actor:
other_queue = await Actor.open_request_queue(name='old-queue')
# ...
In the JavaScript API client as well as in Python API client, you can access a request queue using its respective client. Once you've opened the request queue, you can use it in your crawler or add new requests like you would do with a queue from your current run.
- JavaScript
- Python
const otherQueueClient = apifyClient.requestQueue('jane-doe/old-queue');
other_queue_client = apify_client.request_queue('jane-doe/old-queue')
The same applies for the Apify API - you can use the same endpoints as you would normally do.
Check out the Storage overview for details on sharing storages between runs.
Limits
- The maximum length for request queue name is 63 characters.
Rate limiting
When managing request queues via API, CRUD (add, get, update, delete) operation requests are limited to 400 requests per second per request queue. This helps protect Apify servers from being overloaded.
All other request queue API endpoints are limited to 60 requests per second per request queue.
Check out the API documentation for more information and guidance on actions to take if you exceed these rate limits.